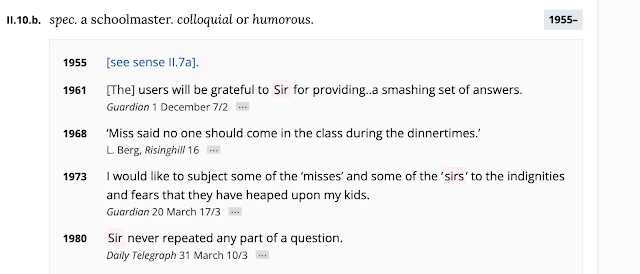
CHOC chocolate (informal, countable)CHOLLA a spelling of challah (the bread)
CLAG mud; more common is claggy for 'having a mud-like consistency'
COLOUR -or/-our
COMPO in military slang, packaged rations; in general English, composite building material; in Aus/NZ worker's compensation
CONNEXION this is a very outdated spelling of connection. Not actually used in UK these days, but wouldn't it be nice to be able to play it?
COOTCH a hiding place, a shed or similar (from Welsh cwtch)
COPPICE a (formerly) wooded area, where the trees have been cut back to encourage growth; or the act of cutting them back
COUNCILLOR post on double Ls
CRAIC it's really an Irish one (a 'good time'), but it qualifies here because it's used more in BrE than AmE (and understood pretty universally in UK)
CRIM criminal
CUTTY short (in some UK dialects)
DADO as in dado rail, what's often called a chair rail in AmE (here's a picture)
DEFENCE AmE defense
DEMOB /DEMOBBED de-mobilize(d); that is, released from the (BrE) armed forces / (AmE) military
DENE a valley (esp. a narrow, wooded one) or a low sand dune near the sea (regional)
DEVILLED post on double Ls
DIALLING post on double Ls
DIDDY small (dialectal); see this old post
DOBBED / DOBBING actually Australian, dob = to inform on someone; see this old post on the BrE equivalent grass (someone) up
DODDLE it's a doddle = (orig. AmE) it's a piece of cake (very easy)
DODGILY adverb form of dodgy, which is in the Bee
DOOLALLY out of one's mind
EQUALLED post on double Ls
FAFF / FAFFING / FAFFS one of the most useful BrE words. See this old post.
FARL a kind of (AmE) quick bread, usually cut into triangles; can be made of various things, but here's a recipe for a common kind, the potato farl
FAVOUR -or/-our
FILMIC cinematic, relating to film
FILO = phyllo (pastry)
FITMENT = AmE fixture, i.e. a furnishing that is fit(ted) in place
FLANNELETTE = AmE flannel old post on flannels
FLANNELLING form of the verb meaning 'to flatter'
FLAVOUR -or/-our
FLAVOURFUL -or/-our
FLORIN a British coin from the pre-decimalization era
FOETAL AmE (and BrE medical) fetal
FOOTMAN a servant or (formerly soldier (of a particular rank)
FUELLED post on double Ls
FULFIL post on double Ls
FUSSBALL [pronounced Germanly] = foosball (table football)
GADGIE / GADGE guy, man, boy (regional)
GAMMON this post covers the 'meat' meaning, but lately it's also used as an insult for Brexiteers and their political similars
GAMMY (of a body part) not working well; e.g. I have a gammy knee
GANNET a type of sea bird, but also BrE slang for a greedy person
GAOL now less common spelling for jail
GHYLL alternative spelling of gill, a northern dialectal term for a ravine [not really all that common—all the dictionaries prefer the simpler spelling]
GIBBET gallows; to hang (a person) [not really in current use]
GIFFGAFF now better known as the name of a mobile phone company, it's an old slang word meaning 'mutual assistance' or 'banter'. (Oxford hyphenates it, but Merriam-Webster doesn't)
GIGGED / GIGGING to perform at a gig [playable as of May 2023]
GILET covered at this clothing post and also at this pronunciation post
GIPPING form of gip, a synonym of BOAK (see above)
GITE French, but used in English for a type of holiday/vacation cottage
GOBBED / GOBBING form of gob, which as a noun means 'mouth', but as a verb means 'spit'
GOBBIN waste material from a mine
GOBBY mouthy
GOOLY (more often GOOLIE, GOOLEY) a testicle (informal, see GDoS)
 |
| getting gunged/slimed |
GUNGE any unpleasant soft or slimy substance; also used as a verb for having such stuff poured over one's head on a children's show (= AmE slime)
GURN / GURNING see this old post
HAITCH = AITCH, but pronounced differently See this old post.
HALLO old-fashioned hello
HENCH strong, fit (like a weightlifter)
HOLDALL a duffel bag or similar heavy-duty bag; often spelled with a hyphen (hold-all), but at least some places don't.
HOOPOE a kind of bird (mostly African), which sometimes makes it to England
HOGMANAY it is a proper noun, but I wanted to include it anyway
HOICK / HOIK to lift/pull abruptly
HOTCHPOTCH AmE hodgepodge
INNIT invariant tag question: isn't it?
INVIGILATING AmE proctoring; old post
JAMMY lucky; old post
KIRK church (Scotland)
KIPPING form of kip, to take a nap
LAIRY (esp. of a person) unpleasantly loud, garish
LAMBING form of to lamb, give birth to lambs. Often heard in lambing time or lambing season
LAMPED form of to lamp, to hit a person very hard
LARKING form of to lark, 'to behave in a silly way for fun'
LAVVY lavatory (informal)
LAYBY AmE turnout (and other synonyms/regional terms); a place where a car can move out of the flow of traffic (usually has a hyphen lay-by, but I found one dictionary that doesn't require it)
LICENCE is the noun form of the verb license in BrE; in AmE, both are license
LIDO an outdoor public swimming pool; there's some debate about how to pronounce it
LILO a blow-up mattress for floating on in a pool
LINO short for linoleum
LOLLY lollipop or (AmE) popsicle (especially in ice lolly)
LOVAGE a(n) herb that Americans don't see very often [has been added! Played successfully on 3 May 2023]
LUPIN AmE lupine, a flower
LURGI / LURGY see this old post
MEDIAEVAL the less common spelling of medieval
MILLIARD (no longer really used) a thousand million, i.e. a billion
MILORD address term for a nobleman
MINGE a woman's pubic hair/area (not flattering)
MINGING foul, bad smelling, ugly (rhymes with singing!)
MOANY apt to moan
MODELLED post on double Ls
MOGGY a cat (informal)
MOOB man boob
MOTTE part of a motte-and-bailey castle
MOULT AmE molt (related to -or/-our)
MOZZIE mosquito
MUPPET in its lower-case BrE sense: 'idiot; incompetent person'
NAFF this has come up in posts about 'untranslatables' and about a study that identified common BrE words Americans don't know
NAPPY AmE diaper
NAVVY a manual labo(u)rer (old-fashioned)
NEEP Scottish English for what the English call a swede and what Americans call a rutabaga (old post on the latter two)
NELLY in the BrE phrase not on your nelly (= AmE not on your life)
NIFFY unpleasant-smelling
NOBBLE to unfairly influence an outcome; steal
NOBBLY alternative spelling of knobbly (which is more common in both AmE & BrE)
NONCY adjective related to nonce (sex offender, p[a]edophile)
NOWT nothing (dialectal)
ODOUR -or/-our
OFFENCE AmE offense
OFFIE short for BrE off-licence; AmE liquor store (discussed a little in this old post)
OPPO informal (old-fashioned) a colleague or friend
ORACY the speaking version of literacy; in US education, it's called orality
PACY having a good or exciting pace (e.g. a pacy whodunnit)
PAEDO short for pa(e)dophile
PANTO see this post
PAPPED / PAPPING from pap, to take paparazzi pictures
PARLOUR -or/-our
PARP a honking noise
PEDALLED post on double Ls
PELMET another one from the study that identified common BrE words Americans don't know
PENG slang for 'excellent'
PHOTOCALL an occasion when celebrities pose for photos
PICCALILLI a mustard-based relish
PIEMAN / PIEMEN this one is usually two words (pie man), but I was able to find a dictionary that allowed it as a single word, so I added it to the list
PIPPED / PIPPING pip = to defeat by a small amount; often heard in to be pipped at the post
PITTA another spelling for pita, more in line with the BrE pronunciation of the word
PLAICE another one from the study that identified common BrE words Americans don't know
PLUMMY see this post
PODGY chubby
POMMY another Australian one, but English people know it because it's an insult directed at them, often in the phrase pommy bastard
PONCE / PONCY see this post
PONGING horrible-smelling
POOED / POOING see this post for the poo versus poop story
POOTLE to travel along at a leisurely speed
POPPADOM / POPPADUM anything to do with Indian food is going to be found more in UK than US
PORRIDGY like porridge, which in AmE is oatmeal
PUFFA full form: puffa jacket; a kind of quilted jacket; it is a trademark, but used broadly; I did find it in one dictionary with a lower-case p
PUNNET see this old post
QUIETEN, QUIETENING AmE uses quiet as a verb
RAILCARD you buy one and it gives you discounts on train tickets
RANCOUR -or/-our
ROTA a list of who's doing what when—e.g. a cleaning rota ROLLMOP pickled herring fil(l)et wrapped around a filling
RUMOUR -or/-our
TANNOY AmE loudspeaker, public address system (originally a trademark, but now used generically)
TARTY dressed (etc.) in a provocative manner
TELLY (orig.) AmE tv
TENCH a Eurasian fish
THALI another Indian menu word
THICKO stupid person
TIDDY small (dialectal)
TIFFIN usually referring to chocolate tiffin (recipe)
TINNING AmE canning
TITBIT see this post
TITCH a small person
TIZZ = tizzy (to be in a tizz[y])
TOFF an upper-class person (not a compliment)
TOMBOLA see this post
TONTINE a kind of investment scheme that pays an annuity
TOTTED / TOTTING see this post
TOTTY an objectifying term for (usually) a woman
TRUG a kind of basket; these days, often a handled rubber container
TUPPENCE two pence
TWIGGED, TWIGGING form of twig 'to catch on, understand'UNEQUALLED post on double Ls
UNVETTED related to my 2008 Word of the Year
VALOUR -or/-our
VIVA an oral exam (short for viva voce)
WAIN archaic a cart (kept alive by the fame of Constable's painting The Hay Wain)
WANK / WANKING my original Word of the Year (2006!)
WEEING AmE peeing
WELLIE / WELLY a (BrE) wellington boot / (AmE) rubber boot
WHIN a plant (=furze, gorse)
WHINGE AmE whine (complain) [now playable]
WIGEON a kind of duck (there are American and European wigeons, but for some reason the British talk about them more than Americans do, so it shows up in the British corpus more)
WILLIE / WILLY penis
WOAD a plant used to make blue dye
WOLD a clear, upland area (mostly in place names now)
WONGA slang: money
WOOLLEN post on double Ls
YOBBO / YOBBY hooligan / hooliganish
YODELLED post on double Ls
YOICK to cry out yoicks! in fox-hunting (not exactly common, but it's in a dictionary)