Baking and baked goods are a perennial source of US/UK miscommunication—in large part because most of our current baking/eating habits were only invented after the split between American and British English. We eat different baked goods with newish names and we often use the same old words in different new ways.
While I've written
many posts that have mentioned cake (see links below), I've come to
feel the need for a much bigger one about cake. This one has been several (very busy) months in the making.
cake itself
The word cake came into English from Old Norse (or another Scandinavian source) in around the 13th century. Way back then it was a word for a round loaf of bread that was a bit flattened by having been turned over while baking. These days we associate it more with sweet baked goods, usually (but not necessarily) those leavened with something other than yeast. But its round, bready roots come through in things like (Scottish) oatcake (which refers to something more like modern crackers than like modern cakes) and northwestern England's barm cakes, one of the many regional names for the kinds of bread rolls with which you might make a sandwich (in the American sense). Later, cake came to mean any round, flattened food, and thus we have fish cakes and crab cakes and rice cakes and the like.
People only started using cake as a mass noun referring to the substance (rather than the loaf as a whole) in the 16th century, and from then it increasingly referred to fancy or sweet bread-like things.
Cake v dessert/pudding
Many Americans would think of cake as a rather normal dessert. But those who've watched the Great British (orig. AmE) Bake Off (GBBO) will have seen that cake and dessert are
treated as different things. Such is the case in English culture (at
least) more generally. Cake is something you'd have with coffee or tea
as a break, not something you'd immediately think of preparing for the
final course of a meal. (Though you will find the occasional cake on a UK
dessert menu.) As we've already seen in the dessert/pudding post, puddings are another matter. Some look and feel like cakes (e.g., my fave sticky toffee pudding), but are not usually considered cakes in BrE. (Please do go to the pudding post, linked above, if you want to comment on puddings.)
Cake(s) as sweet baked snacks
On the other hand, in certain contexts, all sorts of things can loosely count as cake in England that would not be so called in AmE. Say you went to a coffee shop with your friend. If you were English you might ask them "Which cake do you want?" And your English friend might say "A (orig. AmE) brownie" or "The apple turnover, please" or "The carrot cake, please". If you were American, and you wanted the brownie or the turnover, you'd probably answer that question with "I'm not in the mood for cake, but I'd like that brownie/apple turnover." For Americans, cakes are cakes and other baked goods are other baked goods. For the English, cake can be an umbrella term for sweet baked goods eaten in the situations where one usually eats cakes in the narrower sense. (NB: I'm saying English rather than British because not enough Scottish or Welsh people have offered to buy me cake in coffee shops. More fieldwork needed.)
If I were Americanly asking someone which thing they wanted in the coffee shop, I'd probably say "Which kind of cake do you want?" because "which cake" doesn't really sound right in AmE, where it more usually refers to a big thing that you slice and not an individual serving of it. If a BrE speaker had a cake with their tea, it would fit on a small plate (under which the server will have inexplicably placed a paper napkin as if it's a doily, rendering the napkin useless—a coffee-shop peeve of mine). If an American had a cake with their coffee, they'd be an incredible glutton, eating enough for a dozen people.
AmE snack cake
refers to the overly processed small cakes that are packaged for putting in
lunch boxes. Twinkies are a famous example, but there are lots of other
kinds as well (here's a guide).
You can get such individually wrapped cakes in the UK too, e.g. Cadbury
Mini Rolls are pretty much the equivalent of a Hostess Ho-Ho and the Mr
Kipling brand offers a variety of such products, but I don't know of a generic BrE term
for them. But again, we'd call them a snack cake but probably not a cake.
Update, 16 Feb: Here's a great illustration of the BrE cakes = 'sweet baked snacks' meaning. I took this photo at a campus café, where they were trying to offload baked goods before the weekend. The sign reads "All cakes £1.00" and all those things in the picture counted as cakes for the purposes of the £1 promotion. These include (if you can't see them): cookies, flapjacks, millionaire's shortbread (and possibly some other tray bakes [see below]), (American-style) muffins, and filled and unfilled croissants. In AmE, you'd need to say "all baked goods" or something like that, rather than "all cakes".
Types of cake
A very noticeable thing if you watch GBBO is the constant reference to sponge. Americans can use the term sponge cake (emphasis on the cake) but don't use it often because that's the prototypical cake type—and you don't need to specify the most typical type. (I've discussed the psycholinguistic concept of prototypes here.) It'd be like saying cloth shirt—almost redundant.
[Update: see the comments for some more-informed American takes on sponge, which seem to indicate that for AmE sponge is a method (making with egg whites, not butter) and for BrE it's a result (a spongy texture). This fits beautifully with other examples of Americans naming things in reference to the form of the ingredients (pre-assembly) and British using names relating to the form of the result. See previous discussions of mashed potato(es) and scrambled egg(s) and burgers and hot dogs for other examples.]
But BrE speakers are more likely to call it sponge than to call it sponge cake, if that's the kind of cake they're talking about. A Victoria sponge (aka Victoria sandwich) is a two-layer cake with jam (and often cream) in the middle (no icing/frosting on top)—a very common cake in England. On GBBO they talk about lots of different types of sponge, like genoise or joconde, but that's specialist jargon that you don't tend to hear elsewhere. If you want more about those, see this Wikipedia entry.
 |
| from Meg Rivers Bakers |
A reason that BrE speakers need to talk about sponge is that it's not necessarily the default cake type. Fruit cakes are very traditional and (get ready for a shocker, Americans) even loved in England. You cannot imagine my disappointment the first time I was handed a slice of English wedding cake and discovered it wasn't a nice, white sponge cake like I was expecting, but a fruit cake as in the photo to the left. When I got married in England, I had to insist that one of our cake's layers was not fruit. I didn't care what it was, as long as it wasn't fruitcake.
(A note on spelling: AmE prefers fruitcake and BrE goes both ways: fruit cake or fruitcake.)
The
traditional English Christmas cake is also a fruit cake. This has been
adopted to a small degree in the US, where there is some tradition of
giving fruitcakes as Christmas gifts. (When/where I was a kid, the
local Lions Club sold them as Christmastime fundraiser. It seems they still do in New Zealand.) But Americans also have the tradition of mocking fruitcakes as the worst cake and the worst gift, starting with Johnny Carson in 1973: "The worst gift is a fruitcake. There
is only one fruitcake in the entire world, and people keep sending it
to each other." American fruitcakes are generally
unfrosted/uniced, whereas English Christmas cakes have white royal
icing (see link) and decoration.
While there aren't as many cake mixes in the UK, there are a lot of long-life
ready-made cakes in boxes. (Something that surprised me when I moved to England.) The popularity of one supermarket chain's
Colin the Caterpillar cake (the birthday cake for one side of my UK family) gave rise to the 'generification' of the caterpillar cake, which gave rise to lawsuits and news stories last year. (Click on the last link for pictures.)
Another cake type I've tweeted about a lot is coffee cake:
Difference of the Day: 'coffee cake' In AmE, a type of cake, often with a cinnamon crumble topping or similar, that's meant to be eaten with coffee. In BrE, a cake flavo(u)red with coffee. I've done this one before, but I had such a gorgeous AmE one that I had to share: pic.twitter.com/UKK7omY6aO
— Lynne Murphy (@lynneguist) April 9, 2018
Other US cake types include (links are to Wikipedia):
- angel food cake (a very light sponge made with egg whites and cream of tartar—an ingredient that seems to show up in US baking a lot more than UK baking)
- devil's food cake, which would probably be called chocolate fudge cake in BrE
- pound cake, which isn't necessarily American, but it's much more common in the US—and thus shows up nearly seven times as much in AmE as BrE in the GloWbE corpus.
On the UK side, one runs into lemon drizzle cake a lot, while in the US one mostly gets lemon cake or lemon bars.
 |
| Image from Wikipedia |
cake accoutrements & shapes
The utensil with which you lift a slice of cake is a cake slice (BrE 1810s) or a cake server (AmE ?1890s).
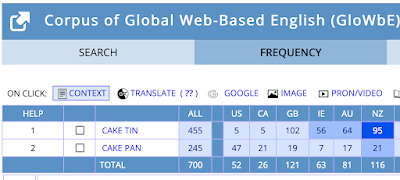
Ring-shaped cakes made in fluted pans/tins are common in Europe, but it's in the US that they came to be known as Bundt cakes, after the trademarked name of a pan sold by the Nordic Ware company. (See Wikipedia for more.)
Sheet cakes also seem to be an AmE invention—these are unlayered, frosted (and often decorated) sponge cakes made in a rectangular pan. People talked about them a bit more after Tina Fey went onto Saturday Night Live to propose "sheet caking" as a method of dealing with far-right demonstrations.
(I must say, though, that her sheet cake seems tall enough that it must be layered.)
In BrE I've seen a sheet cake referred to as a tray bake, but tray bake is used for all sorts of things that are baked in a low, rectangular pan/tin/tray, including the things Americans would call bar cookies. (For past posts about cookies, see here.)
I've written before about AmE cupcake v BrE fairy cake. In BrE today, cupcake has been imported for bigger, fancier ones.
[Late addition, 27 Dec]: I'd thought I'd written here about BrE loaf cakes v American quick breads, but my memory played tricks on me—I must have been remembering writing about it in The Prodigal Tongue. In the book, I use two banana bread recipes as illustration of how many levels AmE and BrE can differ on, and one of the differences is that at one point in the British recipe, the banana bread is called "the cake". Many sweet, loaf-shaped things that Americans bake and might well slice and butter (banana bread, zucchini (BrE courgette) bread, pumpkin bread, ) turn up as [ingredient] loaf cake in UK coffee shops. (When transferred to BrE cake status, they often have icing drizzled over.) Here's a bit of what I wrote in The Prodigal Tongue:
American baking has a traditional category called quick breads, that is, breads leavened without yeast. Quick breads include banana bread, zucchini (= UK courgette) bread, and my mother’s famous pumpkin bread, as well as American biscuits (which look a bit like British scones, but don’t feel or taste like them) and what the British call American-style muffins, including blueberry muffins and bran muffins (though they’ve proved so popular in the UK that the American-style is usually left off these days). In an American cookbook, these recipes are located in the bread chapter. Banana breads and blueberry muffins are relatively new to Britain, and they came over without the larger quick bread category. They thus fell into the cake category.
cake expressions
a piece of cake comes from AmE in the 1960s and means 'easy'. BrE has borrowed it and added a more vulgar version: a piece of piss.
that takes the cake (AmE 1830s) versus that takes the biscuit (BrE
1880s) = 'it is the best/it wins' (though these days it's mostly used
ironically to indicate something that "wins" at being the worst).
off one's cake (BrE informal) = deranged [1880s]; extremely intoxicated [1980s]
bake sale (AmE 1890s) v cake stall (BrE 1600s, but then a more formal business) v cake sale (now more BrE than AmE, but Irish & AmE evidence precedes BrE evidence) = selling donated baked goods as a fundraiser
more links
Before
commenting on this post with comments suggesting or asking questions
about other baked goods, please see these past blog posts. Comments are
welcome on those old posts—conversations on this blog keep on going.
baked goods (misc., includes the usual suspects)
(more on) cookie, (more on) biscuit
molasses, treacle, golden syrup, caramel, toffee (and see the comments there for more on gingerbread)
types of: flour, cream, milk, eggs (that last one's less baking orient(at)ed)
P.S. It's the time of year when I declare the US>UK and UK>US Words of the Year and nominations have been very, very thin this year. Please let me know if you have any nominations for these categories!